What is PE Ratio?
5paisa Research Team
Last Updated: 27 Jun, 2024 06:10 PM IST

Content
- Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E ratio) Definition & Meaning
- What is the PE Ratio?
- Fundamentals of PE Ratio
- How is PE Ratio calculated?
- How to determine the PE Ratio?
- How to Use PE Ratios for Stock Market Investing?
- Understanding the PE Ratio
- Why Do Investors Look at PE Ratios?
- Wrapping Up
Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E ratio) Definition & Meaning
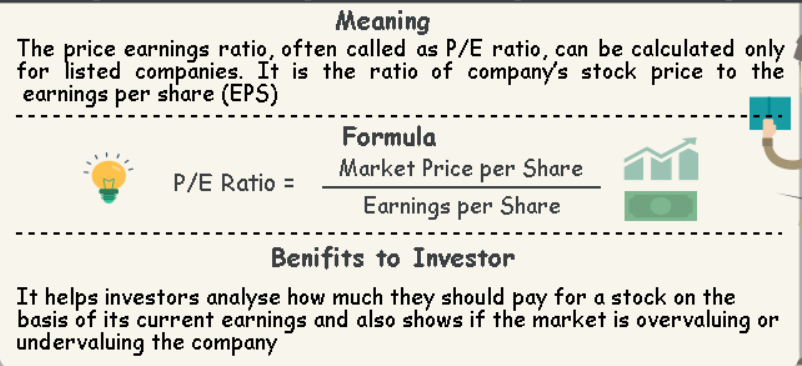
PE ratio stands for the price-earnings ratio. It is a valuation metric that provides investors with information about whether a company's shares are trading at an attractive price given their prospective earnings growth rate.
P/E ratio or price to earnings ratio is one of the most popular valuation tools. But what exactly is the PE ratio?
More About Stock / Share Market
- Difference Between ROCE and ROE
- Markеt Mood Index
- Introduction to Fiduciary
- Guerrilla Trading
- E mini Futures
- Contrarian Investing
- What is PEG Ratio
- How to Buy Unlisted Shares?
- Stock Trading
- Clientele Effect
- Fractional Shares
- Cash Dividends
- Liquidating Dividend
- Stock Dividend
- Scrip Dividend
- Property Dividend
- What is a Brokerage Account?
- What is Sub broker?
- How To Become A Sub Broker?
- What is Broking Firm
- What is Support and Resistance in the Stock Market?
- What is DMA in Stock Market?
- Angel Investors
- Sideways Market
- Committee on Uniform Securities Identification Procedures (CUSIP)
- Bottom Line vs Top Line Growth
- Price-to-Book (PB) Ratio
- What is Stock Margin?
- What is NIFTY?
- What is GTT Order (Good Till Triggered)?
- Mandate Amount
- Bond Market
- Market Order vs Limit Order
- Common Stock vs Preferred Stock
- Difference Between Stocks and Bonds
- Difference Between Bonus Share and Stock Split
- What is Nasdaq?
- What is EV EBITDA?
- What is Dow Jones?
- Foreign Exchange Market
- Advance Decline Ratio (ADR)
- What is F&O Ban?
- What are Upper Circuit and Lower Circuit in Share Market
- Over the Counter Market (OTC)
- Cyclical Stock
- Forfeited Shares
- Sweat Equity
- Pivot Points
- SEBI-Registered Investment Advisor
- Pledging of Shares
- Value Investing
- Diluted EPS
- Max Pain
- Outstanding Shares
- What are Long and Short Positions?
- Joint-Stock Company
- What are Common Stocks?
- What is Venture Capital?
- Golden Rules of Accounting
- Primary Market and Secondary Market
- What Is ADR in Stock Market?
- What Is Hedging?
- What are Asset Classes?
- Value Stocks
- Cash Conversion Cycle
- What Is Operating Profit?
- Global Depository Receipts (GDR)
- Block Deal
- What Is Bear Market?
- How to Transfer PF Online?
- Floating Interest Rate
- Debt Market
- Risk Management in stock Market
- PMS Minimum Investment
- Discounted Cash Flow
- Liquidity Trap
- What are Blue Chip Stocks?
- Types of Dividend
- What is Stock Market Index?
- What is Retirement Planning?
- Stock Broker
- What is the Equity Market?
- What is CPR in Trading?
- Technical Analysis of Financial Markets
- Discount Broker
- CE and PE in the Stock Market
- After Market Order
- How to earn 1000 rs per day from the stock market
- Preference Shares
- Share Capital
- Earnings Per Share
- Qualified Institutional Buyers (QIBs)
- What Is the Delisting of Share?
- What Is The ABCD Pattern?
- What is a Contract Note?
- What Are the Types of Investment Banking?
- What are Illiquid stocks?
- What are Perpetual Bonds?
- What is a Deemed Prospectus?
- What is a Freak Trade?
- What is Margin Money?
- What is the Cost of Carry?
- What Are T2T Stocks?
- How to Calculate the Intrinsic Value of a Stock?
- How to Invest in the US Stock Market From India?
- What are NIFTY BeES in India?
- What is Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR)?
- What is Ratio Analysis?
- What are Preference Shares?
- Dividend Yield
- What is Stop Loss in the share market?
- What is an Ex-Dividend Date?
- What is Shorting?
- What is an interim dividend?
- What is Earnings Per Share (EPS)?
- What is Portfolio Management?
- What Is Short Straddle
- The Intrinsic Value of Shares
- What is market capitalization?
- What is Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP)?
- What is Debt to Equity Ratio?
- What is a stock exchange?
- What are Capital Markets?
- What is EBITDA?
- What is Share Market?
- What is an investment?
- What are bonds?
- What Is a Budget?
- What is Portfolio?
- Learn How To Calculate The Exponential Moving Average (EMA)
- Everything about the Indian VIX
- The Fundamentals of the Volume in Stock Market
- What Is An Offer For Sale, And What Are Its Benefit and Limitations
- Short Covering Explained
- What Is The Efficient Market Hypothesis
- What Is Sunk Cost: Meaning, Definition, and Examples
- What Is Revenue Expenditure? All You Need To Know
- What are operating expenses?
- Return On Equity (ROE)
- What is FII and DII?
- Everything you need to know about the Consumer Price Index
- Everything You Need to Know About Blue Chip Companies
- Know Everything About Bad Banks And How They Function.
- The Essence Of Financial Instruments
- Everything You Need to Know About How to Calculate Dividend per Share
- Double Top Pattern
- Double Bottom Pattern
- What is the Buyback of Shares?
- Trend Analysis
- Stock Split
- Right Issue of Shares
- How To Calculate the Valuation of a Company
- Difference between NSE and BSE
- Learn How to Invest in Share Market Online
- How to select Stocks for Investing
- Do’s and Don’ts of Stock Market Investing for Beginners
- What is Secondary Market?
- What is Disinvestment?
- How to Become Rich in Stock Market
- 6 Tips to Increase your CIBIL Score and Become Loan-worthy
- 7 Top Credit Rating Agencies in India
- Stock Market Crashes In India
- How to Analyse Stocks
- What Is the Taper Tantrum?
- Tax Basics: Section 24 Of The Income Tax Act
- 9 Read-worthy Share Market Books for Novice Investors
- What is Book Value Per Share
- Stop Loss Trigger Price
- Wealth Builder Guide: Difference Between Savings And Investment
- What is Book Value Per Share
- Top Stock Market Investors In India
- Best Low Price Shares to Buy Today
- How Can I Invest in ETF in India?
- What is ETFs in stocks
- Best Investment Strategies in Stock Market for Beginners
- How To Analyse Stocks
- Stock Market Basics: How Share Market Works In India
- Bull Market Vs Bear Market
- Treasury Shares: The Secrets Behind The Big Buybacks
- Minimum Investment In Share Market
- What is Delisting of Shares
- Ace Day Trading With Candlestick Charts - Simple Strategy, High Returns
- How Share Price Increase or Decrease
- How to Pick Stocks in Stock Market?
- Ace Intraday Trading With Seven Backtested Tips
- Are You A Growth Investor? Check These Tips to Increase Your Profits
- What Can You Learn From The Warren Buffet Style of Trading
- Value or Growth - Which Investment Style Can be the Best For You?
- Find Why Momentum Investing is Trending Nowadays
- Use Investment Quotes to Improve Your Investment Strategy
- What is Dollar Cost Averaging
- Fundamental Analysis vs Technical Analysis
- Sovereign Gold Bonds
- A Comprehensive Guide To Learn How to Invest In Nifty In India
- What is IOC in Share Market
- Know All About Stop Limit Orders And Use Them To Your Benefit
- What is Scalp Trading?
- What is Paper Trading?
- Difference Between Shares and Debentures
- What is LTP in the share market?
- What is face value of share?
- What is PE Ratio?
- What is Primary Market?
- Understanding the Difference between Equity and Preference Shares
- Share Market Basics
- How to Choose Stocks for Intraday Trading?
- What is Intraday Trading?
- How Share Market Works In India?
- What are Multibagger Stocks?
- What are Equities?
- What is a Bracket Order?
- What Are Large Cap Stocks?
- A Kickstarter Course: How To Invest In Share Market
- What are Penny Stocks?
- What are Shares?
- What Are Midcap Stocks?
- How to Invest in the Share Market? Tips for Beginners Read More
Disclaimer: Investment in securities market are subject to market risks, read all the related documents carefully before investing. For detailed disclaimer please Click here.