What is Disinvestment?
5paisa Research Team
Last Updated: 07 Jun, 2022 03:54 PM IST

Content
- Introduction
- What is Disinvestment?
- How does Disinvestment work?
- Example of Disinvestment
- Causes of Disinvestment
- Why do companies disinvest?
- What does disinvestment mean for our economy?
- Wrapping Up
Introduction
Disinvestment is the opposite of investment. Disinvestment is an intentional effort to reduce, usually by force, something that was previously invested in. For example, disinvestment happens when a country's government tries to undermine or remove foreign businesses from its country.
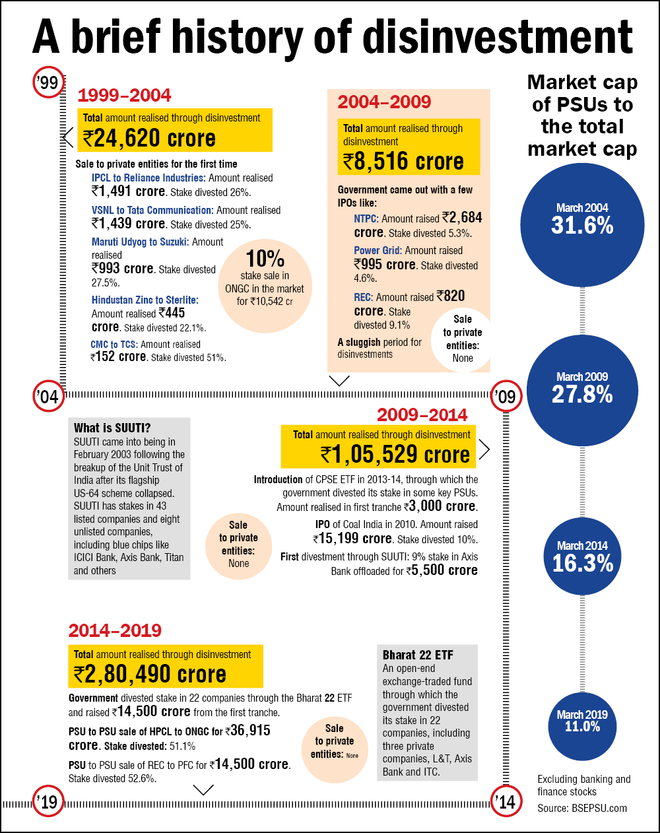
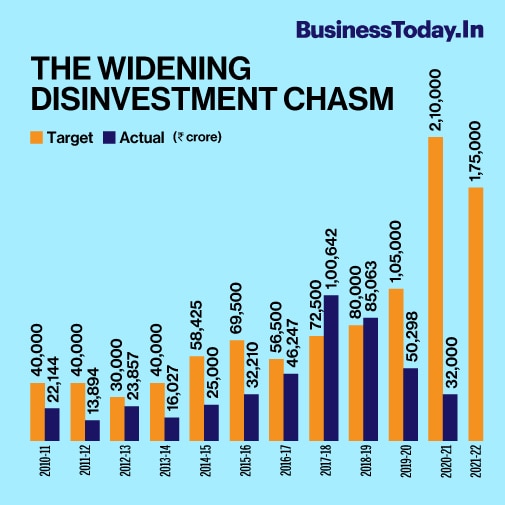
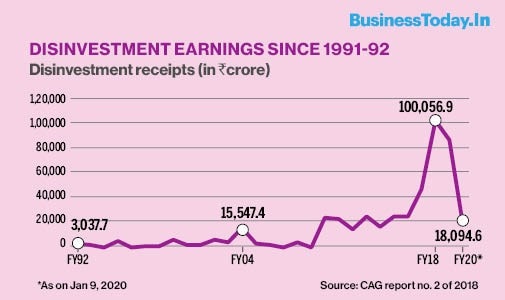
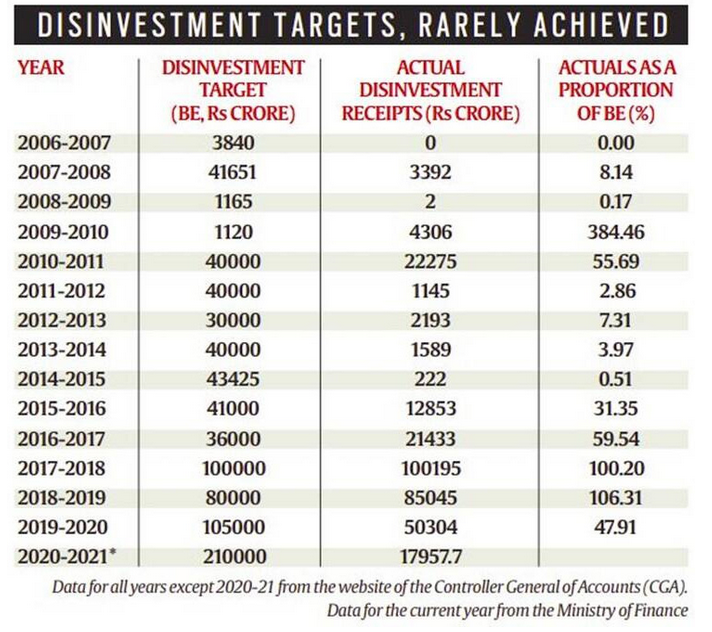
Source : Business Today
Even though disinvestment is often political in nature, it can also be financial. For example, some countries have disinvested from their own companies by selling off their shares. And on a smaller scale, many investors choose to disinvest from companies that they don't think are doing well.
More About Stock / Share Market
- Difference Between ROCE and ROE
- Markеt Mood Index
- Introduction to Fiduciary
- Guerrilla Trading
- E mini Futures
- Contrarian Investing
- What is PEG Ratio
- How to Buy Unlisted Shares?
- Stock Trading
- Clientele Effect
- Fractional Shares
- Cash Dividends
- Liquidating Dividend
- Stock Dividend
- Scrip Dividend
- Property Dividend
- What is a Brokerage Account?
- What is Sub broker?
- How To Become A Sub Broker?
- What is Broking Firm
- What is Support and Resistance in the Stock Market?
- What is DMA in Stock Market?
- Angel Investors
- Sideways Market
- Committee on Uniform Securities Identification Procedures (CUSIP)
- Bottom Line vs Top Line Growth
- Price-to-Book (PB) Ratio
- What is Stock Margin?
- What is NIFTY?
- What is GTT Order (Good Till Triggered)?
- Mandate Amount
- Bond Market
- Market Order vs Limit Order
- Common Stock vs Preferred Stock
- Difference Between Stocks and Bonds
- Difference Between Bonus Share and Stock Split
- What is Nasdaq?
- What is EV EBITDA?
- What is Dow Jones?
- Foreign Exchange Market
- Advance Decline Ratio (ADR)
- What is F&O Ban?
- What are Upper Circuit and Lower Circuit in Share Market
- Over the Counter Market (OTC)
- Cyclical Stock
- Forfeited Shares
- Sweat Equity
- Pivot Points
- SEBI-Registered Investment Advisor
- Pledging of Shares
- Value Investing
- Diluted EPS
- Max Pain
- Outstanding Shares
- What are Long and Short Positions?
- Joint-Stock Company
- What are Common Stocks?
- What is Venture Capital?
- Golden Rules of Accounting
- Primary Market and Secondary Market
- What Is ADR in Stock Market?
- What Is Hedging?
- What are Asset Classes?
- Value Stocks
- Cash Conversion Cycle
- What Is Operating Profit?
- Global Depository Receipts (GDR)
- Block Deal
- What Is Bear Market?
- How to Transfer PF Online?
- Floating Interest Rate
- Debt Market
- Risk Management in stock Market
- PMS Minimum Investment
- Discounted Cash Flow
- Liquidity Trap
- What are Blue Chip Stocks?
- Types of Dividend
- What is Stock Market Index?
- What is Retirement Planning?
- Stock Broker
- What is the Equity Market?
- What is CPR in Trading?
- Technical Analysis of Financial Markets
- Discount Broker
- CE and PE in the Stock Market
- After Market Order
- How to earn 1000 rs per day from the stock market
- Preference Shares
- Share Capital
- Earnings Per Share
- Qualified Institutional Buyers (QIBs)
- What Is the Delisting of Share?
- What Is The ABCD Pattern?
- What is a Contract Note?
- What Are the Types of Investment Banking?
- What are Illiquid stocks?
- What are Perpetual Bonds?
- What is a Deemed Prospectus?
- What is a Freak Trade?
- What is Margin Money?
- What is the Cost of Carry?
- What Are T2T Stocks?
- How to Calculate the Intrinsic Value of a Stock?
- How to Invest in the US Stock Market From India?
- What are NIFTY BeES in India?
- What is Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR)?
- What is Ratio Analysis?
- What are Preference Shares?
- Dividend Yield
- What is Stop Loss in the share market?
- What is an Ex-Dividend Date?
- What is Shorting?
- What is an interim dividend?
- What is Earnings Per Share (EPS)?
- What is Portfolio Management?
- What Is Short Straddle
- The Intrinsic Value of Shares
- What is market capitalization?
- What is Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP)?
- What is Debt to Equity Ratio?
- What is a stock exchange?
- What are Capital Markets?
- What is EBITDA?
- What is Share Market?
- What is an investment?
- What are bonds?
- What Is a Budget?
- What is Portfolio?
- Learn How To Calculate The Exponential Moving Average (EMA)
- Everything about the Indian VIX
- The Fundamentals of the Volume in Stock Market
- What Is An Offer For Sale, And What Are Its Benefit and Limitations
- Short Covering Explained
- What Is The Efficient Market Hypothesis
- What Is Sunk Cost: Meaning, Definition, and Examples
- What Is Revenue Expenditure? All You Need To Know
- What are operating expenses?
- Return On Equity (ROE)
- What is FII and DII?
- Everything you need to know about the Consumer Price Index
- Everything You Need to Know About Blue Chip Companies
- Know Everything About Bad Banks And How They Function.
- The Essence Of Financial Instruments
- Everything You Need to Know About How to Calculate Dividend per Share
- Double Top Pattern
- Double Bottom Pattern
- What is the Buyback of Shares?
- Trend Analysis
- Stock Split
- Right Issue of Shares
- How To Calculate the Valuation of a Company
- Difference between NSE and BSE
- Learn How to Invest in Share Market Online
- How to select Stocks for Investing
- Do’s and Don’ts of Stock Market Investing for Beginners
- What is Secondary Market?
- What is Disinvestment?
- How to Become Rich in Stock Market
- 6 Tips to Increase your CIBIL Score and Become Loan-worthy
- 7 Top Credit Rating Agencies in India
- Stock Market Crashes In India
- How to Analyse Stocks
- What Is the Taper Tantrum?
- Tax Basics: Section 24 Of The Income Tax Act
- 9 Read-worthy Share Market Books for Novice Investors
- What is Book Value Per Share
- Stop Loss Trigger Price
- Wealth Builder Guide: Difference Between Savings And Investment
- What is Book Value Per Share
- Top Stock Market Investors In India
- Best Low Price Shares to Buy Today
- How Can I Invest in ETF in India?
- What is ETFs in stocks
- Best Investment Strategies in Stock Market for Beginners
- How To Analyse Stocks
- Stock Market Basics: How Share Market Works In India
- Bull Market Vs Bear Market
- Treasury Shares: The Secrets Behind The Big Buybacks
- Minimum Investment In Share Market
- What is Delisting of Shares
- Ace Day Trading With Candlestick Charts - Simple Strategy, High Returns
- How Share Price Increase or Decrease
- How to Pick Stocks in Stock Market?
- Ace Intraday Trading With Seven Backtested Tips
- Are You A Growth Investor? Check These Tips to Increase Your Profits
- What Can You Learn From The Warren Buffet Style of Trading
- Value or Growth - Which Investment Style Can be the Best For You?
- Find Why Momentum Investing is Trending Nowadays
- Use Investment Quotes to Improve Your Investment Strategy
- What is Dollar Cost Averaging
- Fundamental Analysis vs Technical Analysis
- Sovereign Gold Bonds
- A Comprehensive Guide To Learn How to Invest In Nifty In India
- What is IOC in Share Market
- Know All About Stop Limit Orders And Use Them To Your Benefit
- What is Scalp Trading?
- What is Paper Trading?
- Difference Between Shares and Debentures
- What is LTP in the share market?
- What is face value of share?
- What is PE Ratio?
- What is Primary Market?
- Understanding the Difference between Equity and Preference Shares
- Share Market Basics
- How to Choose Stocks for Intraday Trading?
- What is Intraday Trading?
- How Share Market Works In India?
- What are Multibagger Stocks?
- What are Equities?
- What is a Bracket Order?
- What Are Large Cap Stocks?
- A Kickstarter Course: How To Invest In Share Market
- What are Penny Stocks?
- What are Shares?
- What Are Midcap Stocks?
- How to Invest in the Share Market? Tips for Beginners Read More
Disclaimer: Investment in securities market are subject to market risks, read all the related documents carefully before investing. For detailed disclaimer please Click here.